In today’s blog, we get technical and answer the burning questions of IT and Networks managers – How does SD-WAN work?
An overview of SD-WAN
How does SD-WAN work and what is it? SD-WAN stands for Software-Defined Wide Area Networking. It’s a way to build a secure wide area network using a software overlay to control, secure access and automate IP connectivity for WAN traffic between offices, suppliers and remote workers.
In today’s era of cloud-enabled networks the key benefits SD-WAN offers are as follows:
- Control
- Automation
- Application Performance
- Security
- Flexibility
- Lower cost Wide Area Network provision
SD-WAN also moves network and security provision from a rule-based configuration to an Intent-based policy-driven network
We will go through the benefits in greater detail later in this blog.
The need of an SD-WAN network is we are now in an era of cloud computing where software (SaaS), telecommunications, and applications run in private and public cloud’s, business needs have changed and so has WAN architecture. Legacy WAN connections such as MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) and standard IPSEC VPN’s no longer have the flexibility to connect our data center’s, branch offices and remote workers into a secure network while ensuring we have access to our cloud applications and have a good user experience for everyone across the network.
In addition, the way we connect to corporate networks has changed, accelerated not only by cloud technology but also by changes brought on by the recent Covid19 pandemic. SD-WAN offers the opportunity to lower costs by removing the need for expensive MPLS links by using cheaper broadband or LTE services to connect your corporate network into a single software-defined WAN wherever you are located.
How does SD-WAN work from a technical perspective?
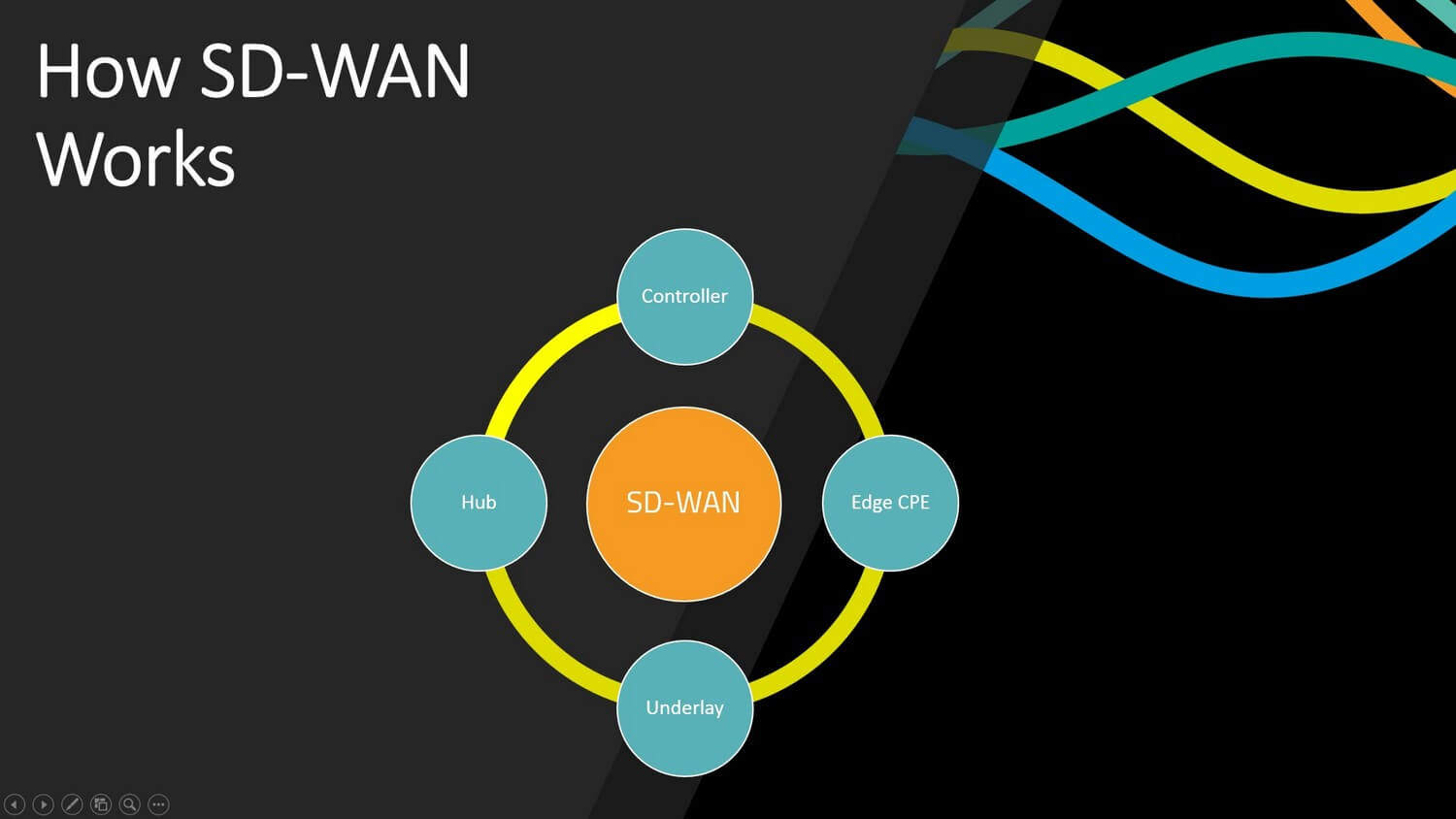
An SD-WAN network has 4 key components, which are as follows:
- An Edge Device or on-premises terminating device which connects the Office or User to the network – usually this would be a router or firewall.
- An SD-WAN Hub is a central point for your remote offices and users to connect in a hub and spoke network topology and is a key part of how application monitoring and WAN optimization is performed.
- An SD-WAN orchestration platform is a network management platform to control your entire network – from endpoints to gateways, to routing, application performance and security.
- An Underlay Network – This is your standard public Internet connectivity, such as 5g or 4g LTE, Wireless, MPLS, Ethernet and broadband services.
Below we have provided a basic network diagram of how a user or office is connected to an SD-WAN network but it is also worth visiting our blog on SD-WAN architecture for an overview of the infrastructure used in a successful SD-WAN deployment
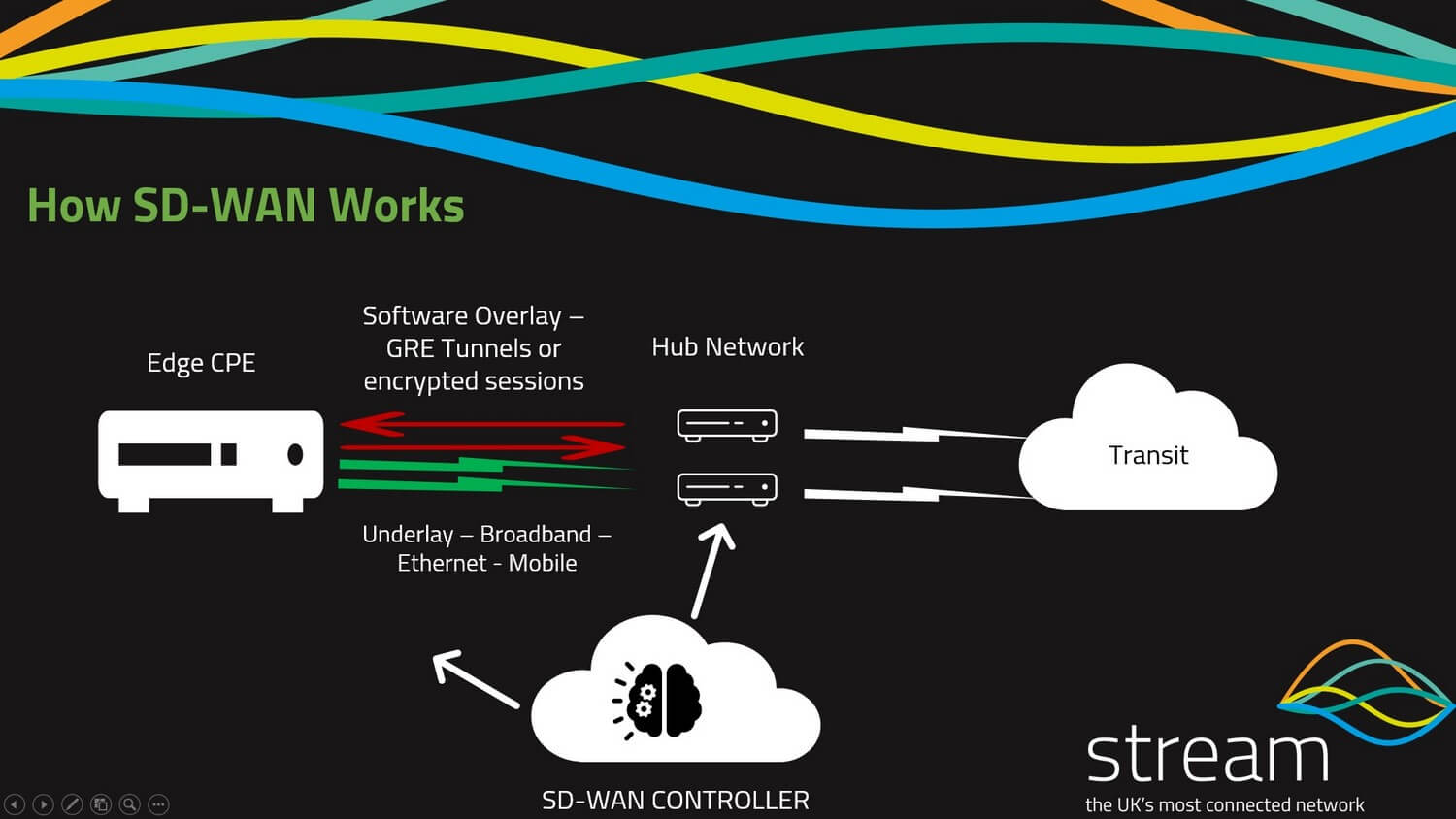
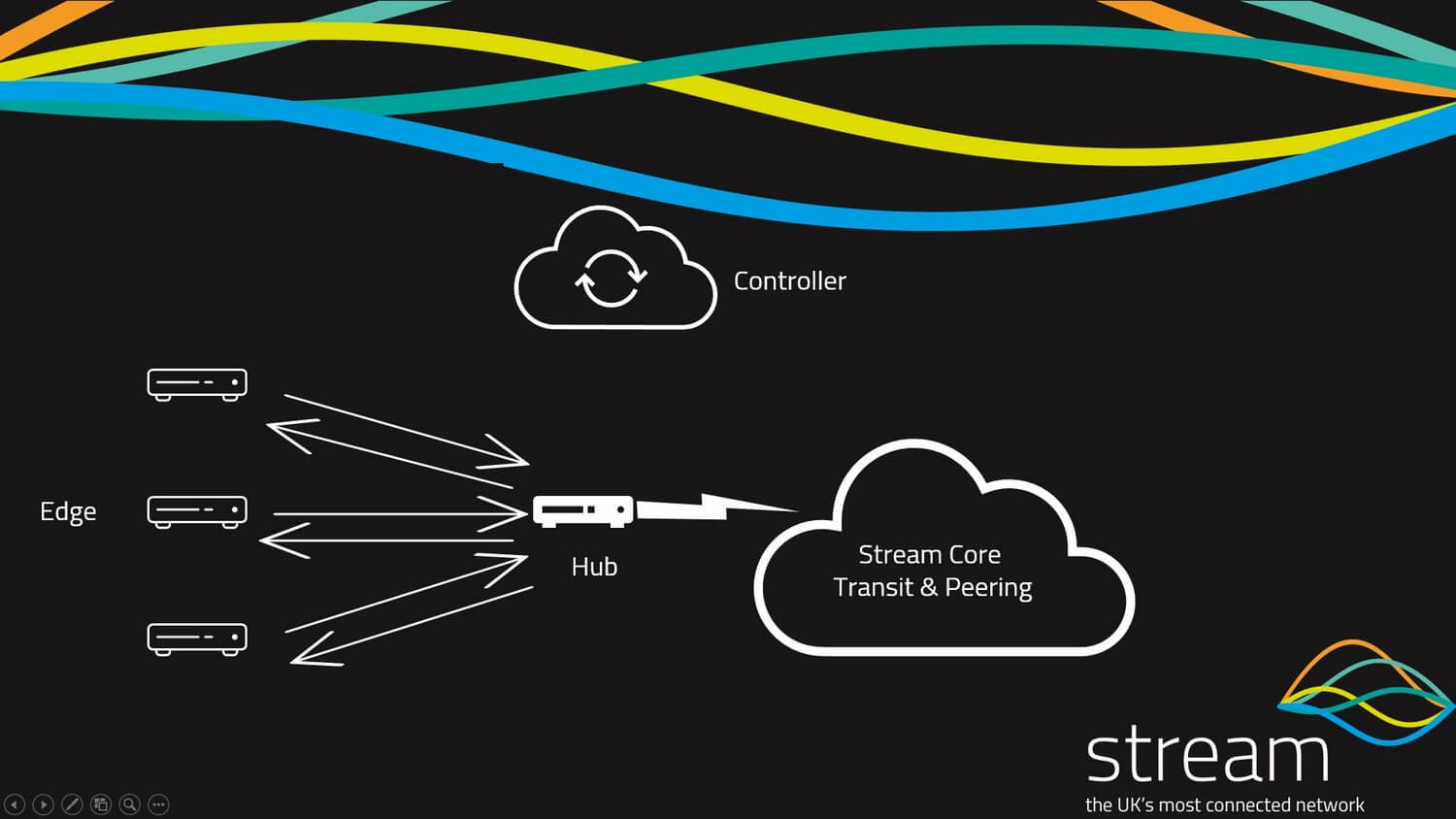
As you can see you have an edge device that has an underlay connection, SD-WAN then creates a software overlay building a secure network to the SD-WAN hub using secure IPSEC GRE tunnels with the SD-WAN service orchestration platform providing centralized management of the network functions, network security, end-user control, and management of critical applications flowing across the network.
So those are the main components or building blocks to deploying an SD-WAN network. However, we want to delve a bit deeper into some of the benefits of SD-WAN technology from technologies such as ZTP (Zero Touch Provisioning) to application control, security, and network monitoring.
What is Network Orchestration?
One of the key elements of an SD-WAN network is the ability to control and manage your entire network from a single pane of glass. With a traditional WAN such as MPLS, you often must rely on your Service Provider to manage the WAN providing no real insight or control plane to your network. With an IP VPN network the bigger the network the more complex it is to manage as each standalone device needs to be managed remotely.
Network orchestration solves these problems by giving you greater control and oversight of your network and reducing the need for IT teams to manage multiple devices by allowing you to control the network from a web-based GUI.
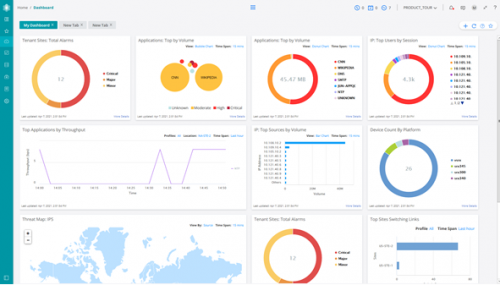
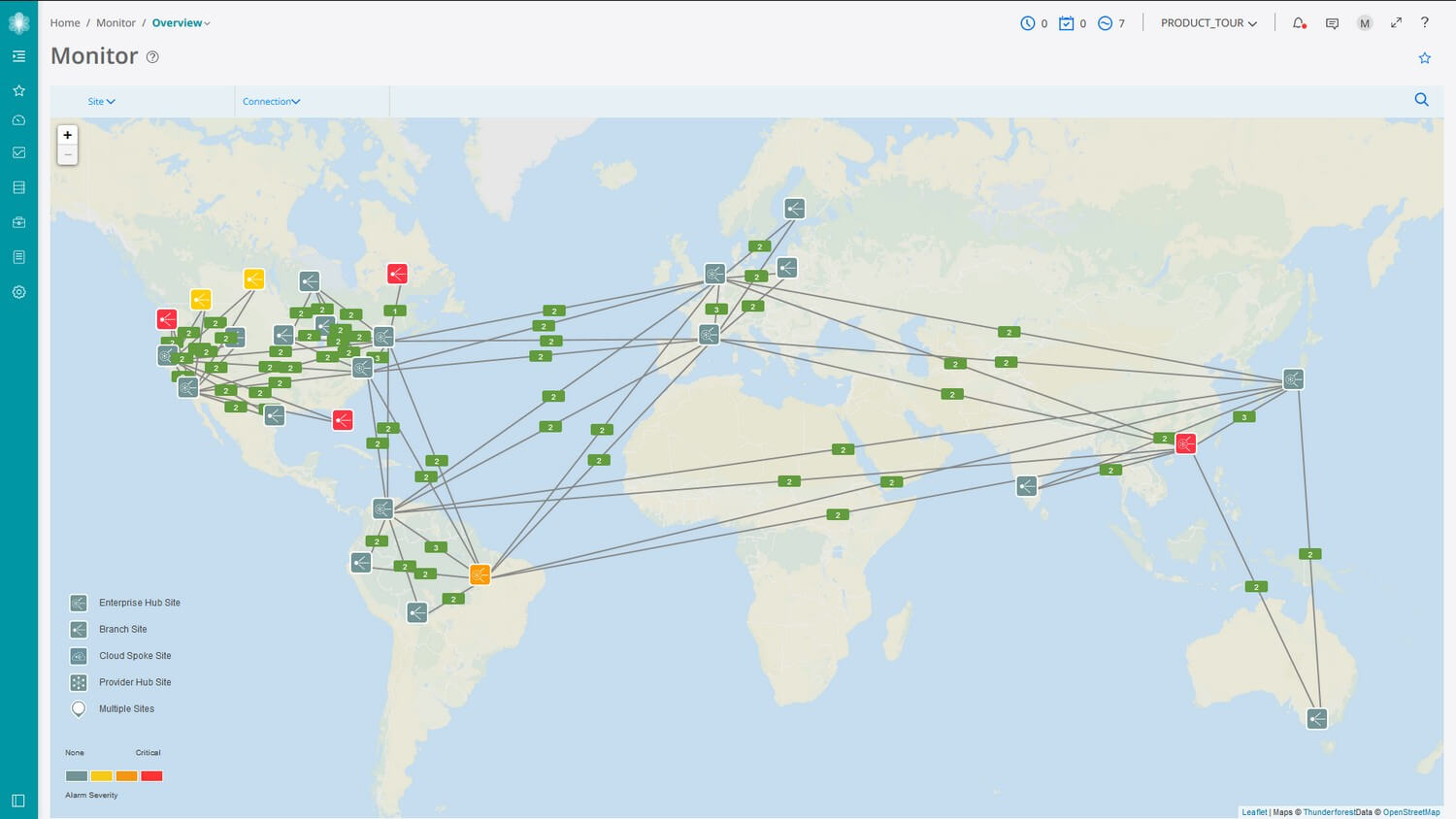
See example of Juniper Contrail Service Orchestrator below.
What is Application Control?
With more and more application traffic being run in the cloud and companies using multiple cloud providers for their IT infrastructure, ensuring users working from a branch office or home has a good quality of experience across the network, to both the cloud and key data center’s is vital to business performance and reduces the need for troubleshooting.
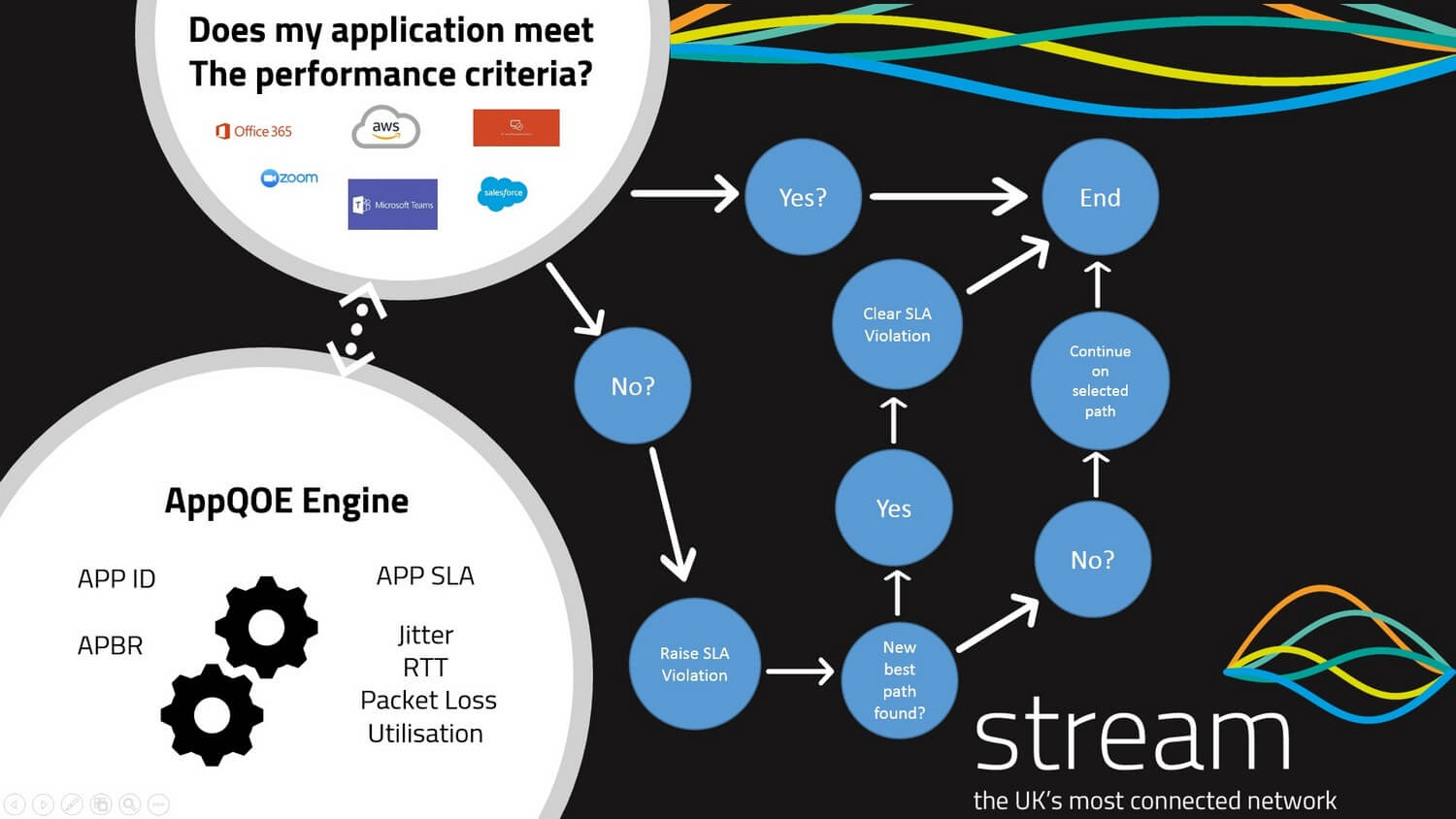
This is where application control using protocols such as APP QOE / QOS come into play by providing network segmentation for applications. Application Quality of Experience or Quality of Service allows you to identify any application traffic across your network and dependant on SLA’s set, allows you to define what happens to that network traffic in the advent of an SLA breach.
For example, you could identify SAAS applications such as O365 or Microsoft Teams and set an SLA based on minimum latency, packet loss, bandwidth utilisation or jitter and if anyone or all the metrics are broken to find a better path on the network for applications to traverse. Application control provides automation and load balancing for all the applications across the network without the need for manual intervention.
What is ZTP – Zero Touch Provisioning?
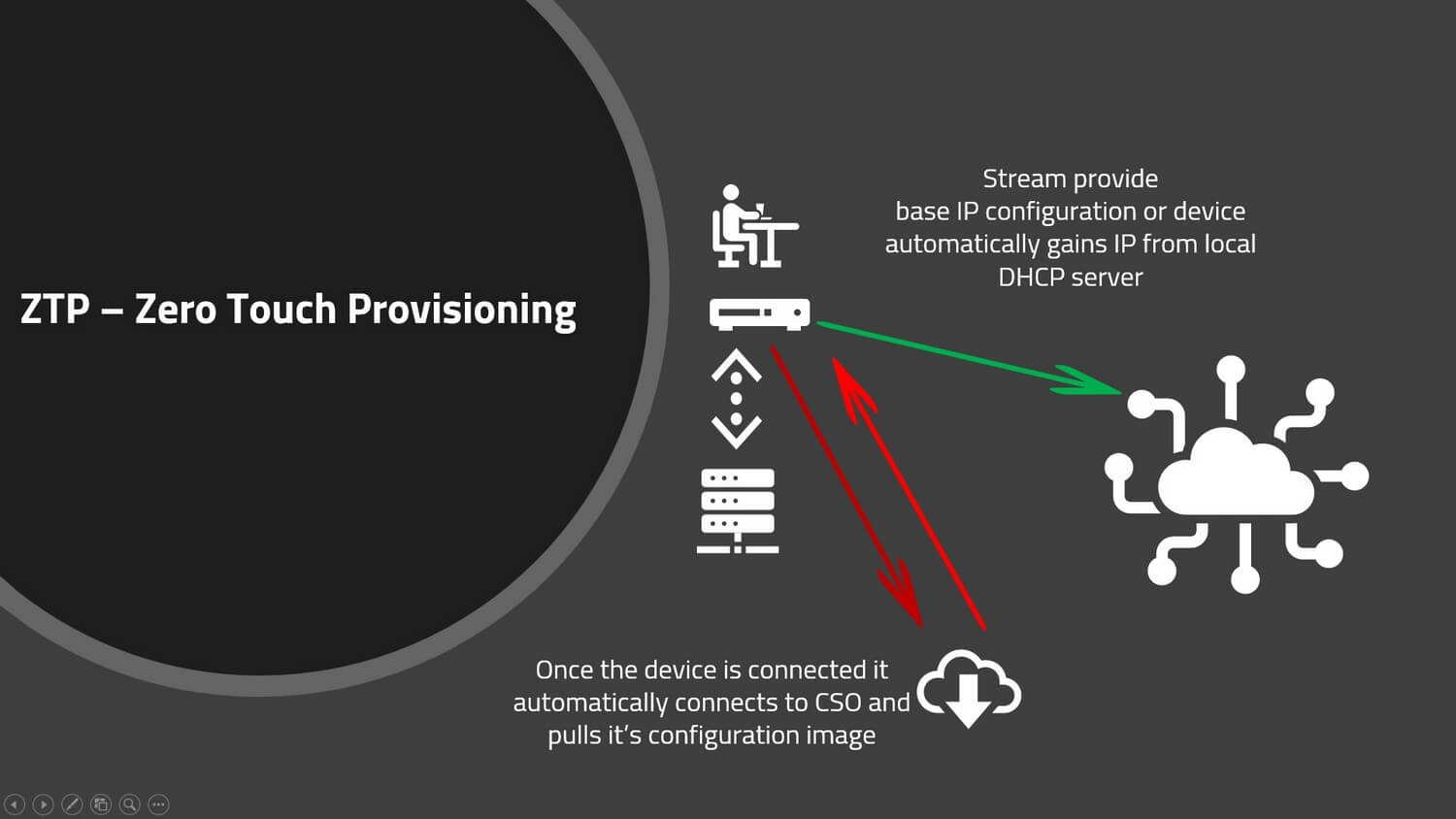
Zero Touch Provisioning allows you to onboard your wan edge routers without the need for an engineer to configure every individual device, this delivers costs savings and reduces the deployment time for new network rollouts.
When rolling out new network infrastructure with ZTP you simply ship the edge device to a home worker or branch location and connect it to the network via DHCP. No pre-configuration of the device is required, the device “calls home” to the SD-WAN orchestrator and downloads its configuration from a pre-configured template.
It also allows you to manage your device operating systems providing the current version of firmware the device has installed and allows you to upgrade it ensuring your network is updated against any security vulnerabilities.
How does SD-WAN provide security?
SD-WAN delivers a secure IPSEC GRE tunnel between every device and user on the network encrypting all traffic from end to end. SD-WAN in most cases also provides next-generation network security built into the SD-WAN hub and edge devices with the ability to configure all traffic to traverse a single point or provide security from every edge device building a Zero Trust Network.
How does SD-WAN provide network monitoring?
SD-WAN provides network monitoring within the Orchestration platform delivering a complete overview of security events, device status, application monitoring including individual user monitoring.
If you are looking at SD-WAN solutions for your business and want advice on use cases or building a Hybrid WAN to ensure your cloud services and real-time applications are secure and have priority across your network, then please contact one of our SD-WAN consultants on 01635 884170.
